We Discover
Natural Sciences
Bactericidal and in vitro osteogenic activity of nano sized cobalt-doped silicate hydroxyapatite
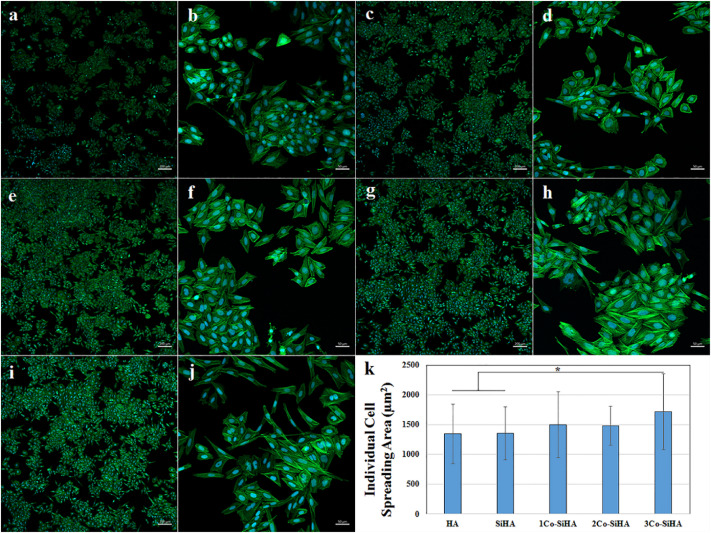
Dr. Ammar Alshemary and his group recently published their results in Ceramics International [IF: 5.2], discusses the antibacterial and bone-forming properties of cobalt-doped silicate hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. In lab settings, these nanoparticles displayed both bactericidal effects and the ability to promote bone growth. This research suggests their potential for medical applications, particularly in orthopedics and bone-related treatments.
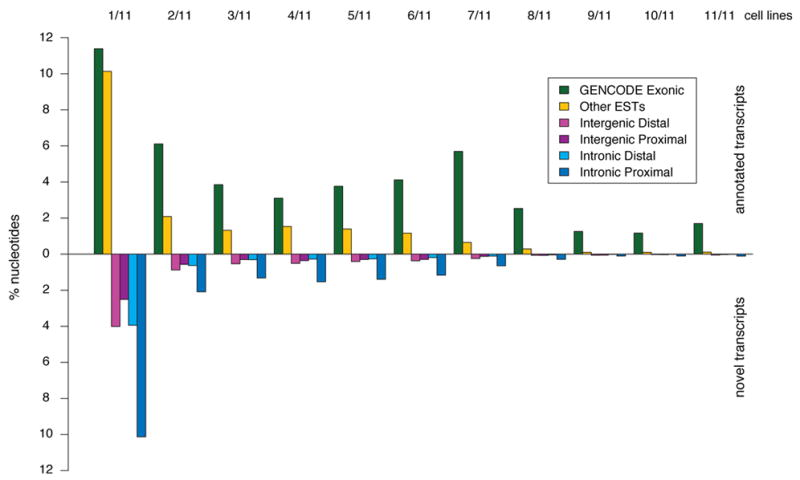
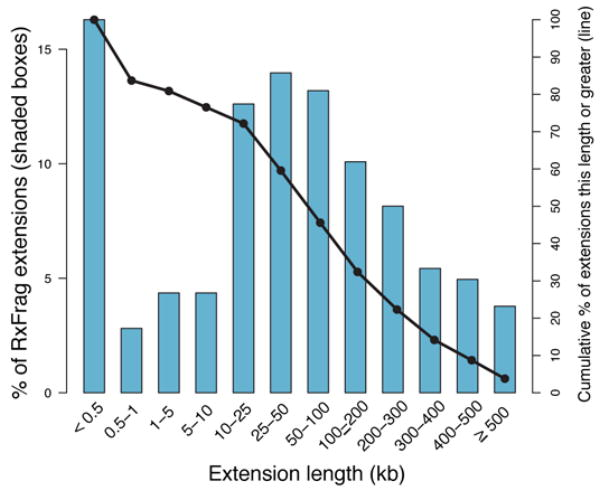
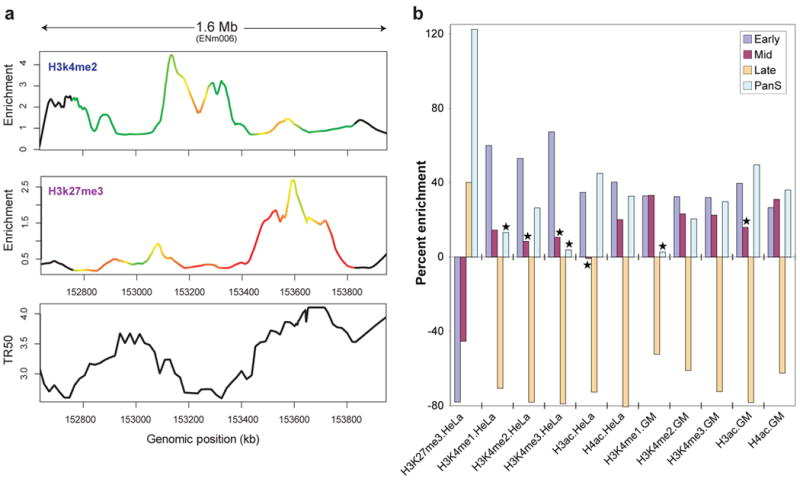
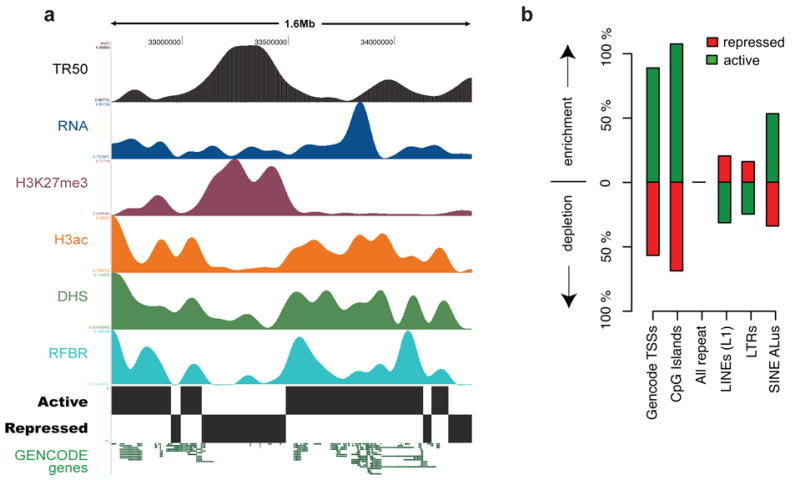
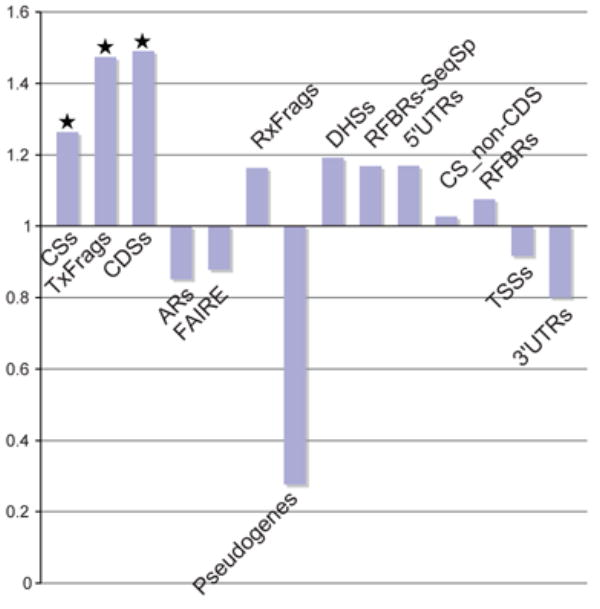
Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the ENCODE pilot project
The ENCODE pilot project conducted by Dr. Siew Woh Choo and his team has published in Nature [IF: 64.8] and analyzed 1% of the human genome to identify and study functional elements. This research aims to understand how genes work and regulate cellular processes. By decoding this small portion of the genome, valuable insights into human biology and disease mechanisms can be gained.
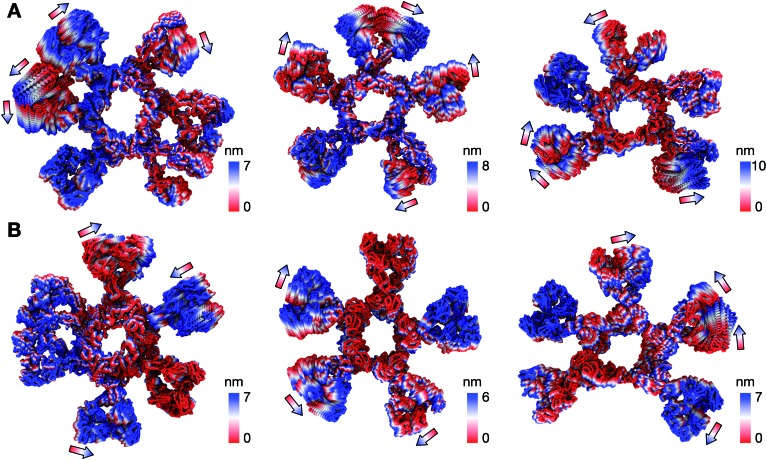
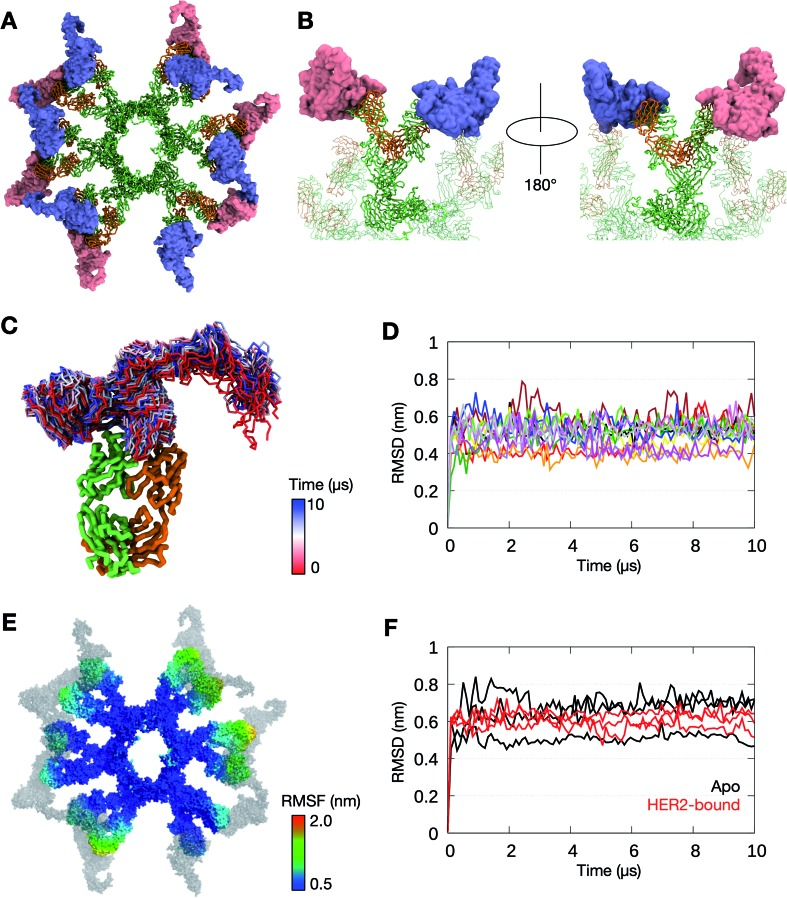
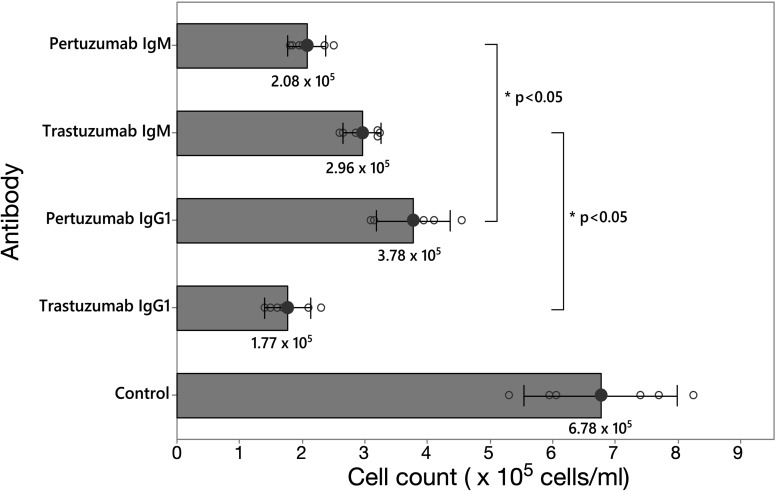
Not all therapeutic antibody isotypes are equal: the case of IgM versus IgG in Pertuzumab and Trastuzumab
Dr. Samual Gan and his team recently published their results in Chemical Science [IF: 8.4], highlights variations in therapeutic efficacy between IgM and IgG isotypes in the antibodies Pertuzumab and Trastuzumab, emphasizing the importance of understanding these differences for optimizing their medical applications and outcomes.
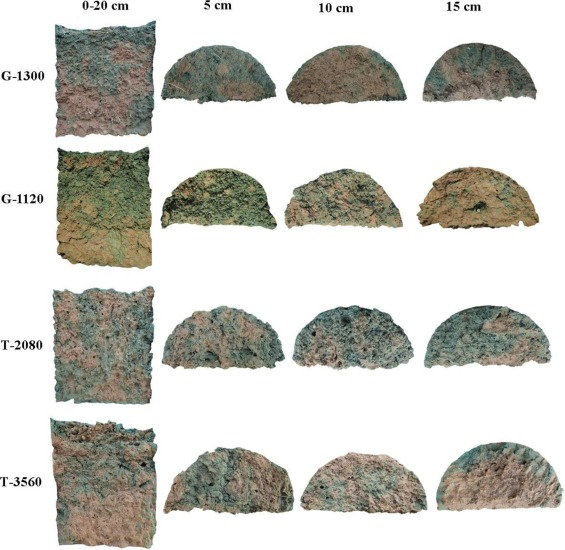
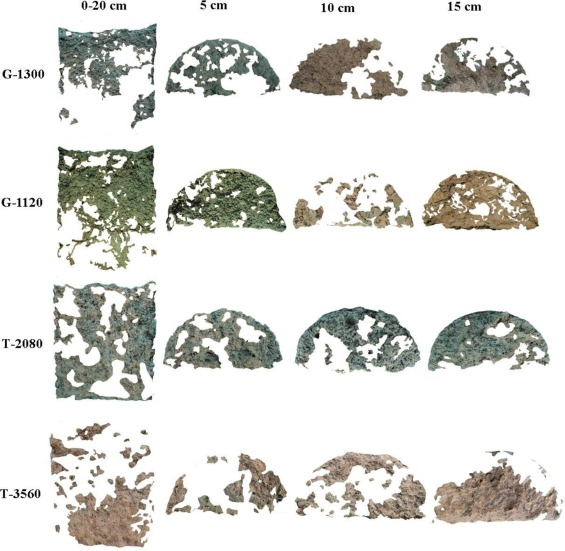
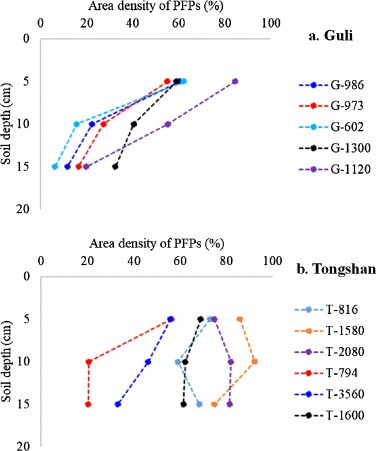
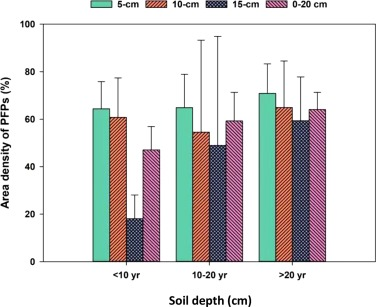
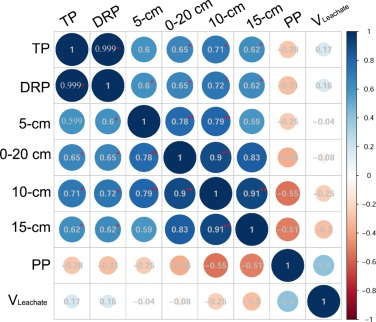
Impact of preferential flow pathways on phosphorus leaching from typical plastic shed vegetable production soils of China
Dr. Yusef Kianpoor Kalkhajeh published paper in AGRICULTURE ECOSYSTEMS & ENVIRONMENT [IF:6.6], explores how preferential flow pathways affect phosphorus leaching in Chinese plastic shed vegetable production soils. It investigates the role of these pathways in phosphorus transport and finds that they significantly contribute to phosphorus leaching, raising environmental concerns related to nutrient runoff in this agricultural context.
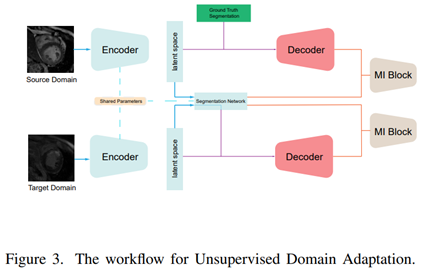
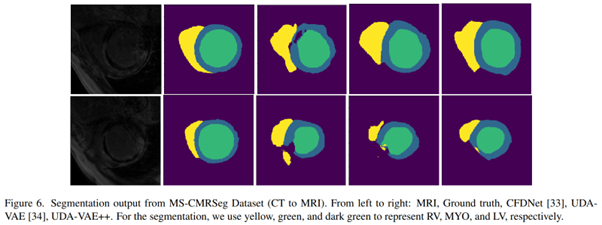
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Cardiac Segmentation: Towards Structure Mutual Information Maximization,
Dr. Gaurav Gupta and his students Shen Zheng and Changjie Lu recently published in the journal Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition [IF: 23.46] and discussed the generalization ability of unsupervised domain adaptive approaches in deep learning under diverse imaging modalities. They developed a novel model SMIE, which uses a global estimator, a local estimator and a prior information matching estimator to maximize mutual information between reconstruction and segmentation tasks. Comprehensive experiments on the benchmark heart segmentation dataset show that the model outperforms previous state-of-the-art techniques in quality and quantity.
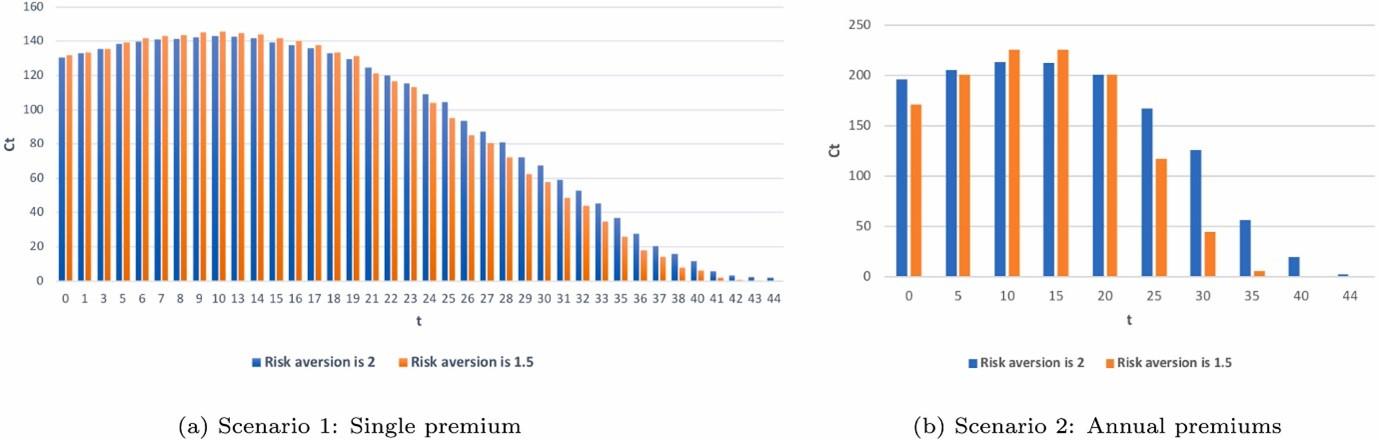
Optimal lifetime income annuity without bequest: Single and annual premiums
Dr. Ebenezer and his team recently published paper in Finance Research Letters [IF: 9.848] about the optimal annuitization, risk-free investment, and consumption problem in a post-retirement lifecycle model without bequest motives. They find out that the effect of allocating wealth to purchase a lifetime income annuity increases with higher risk aversion for a single premium and decreases with residual wealth for annual premiums. Finally, they show that partial annuitization can be optimal for different risk levels.
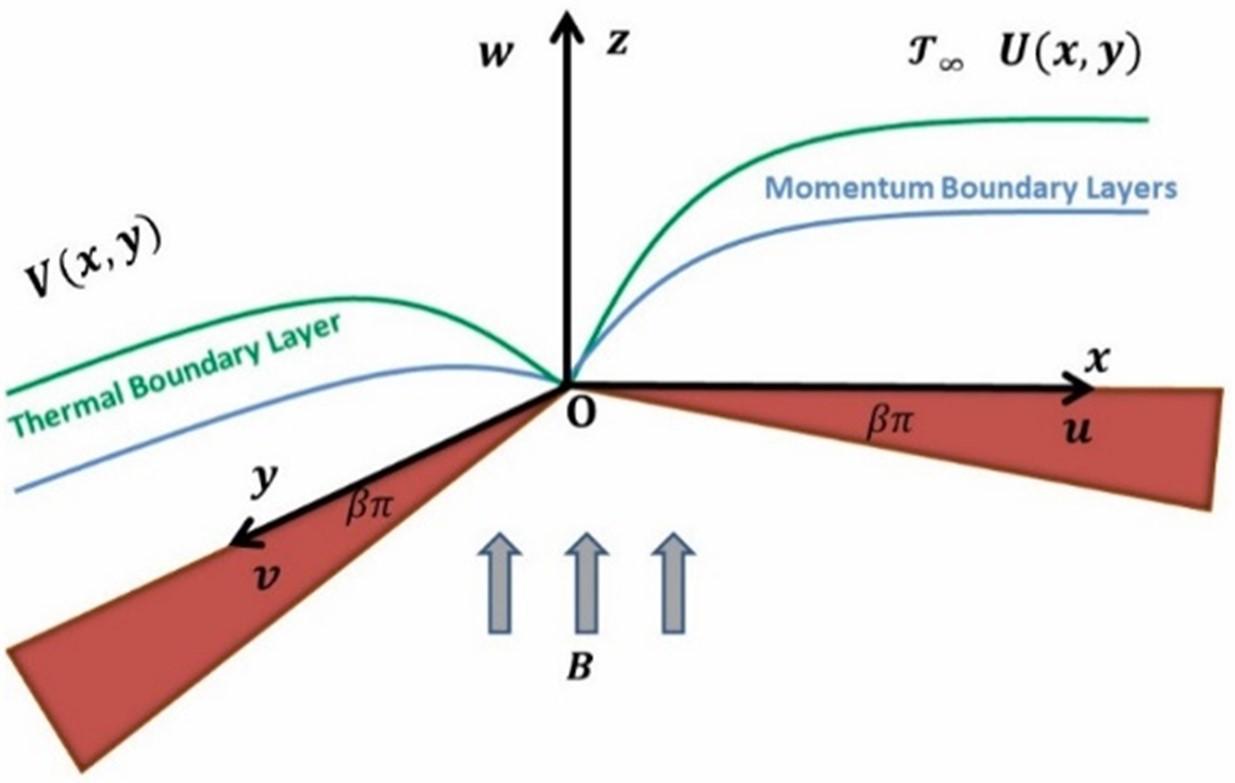
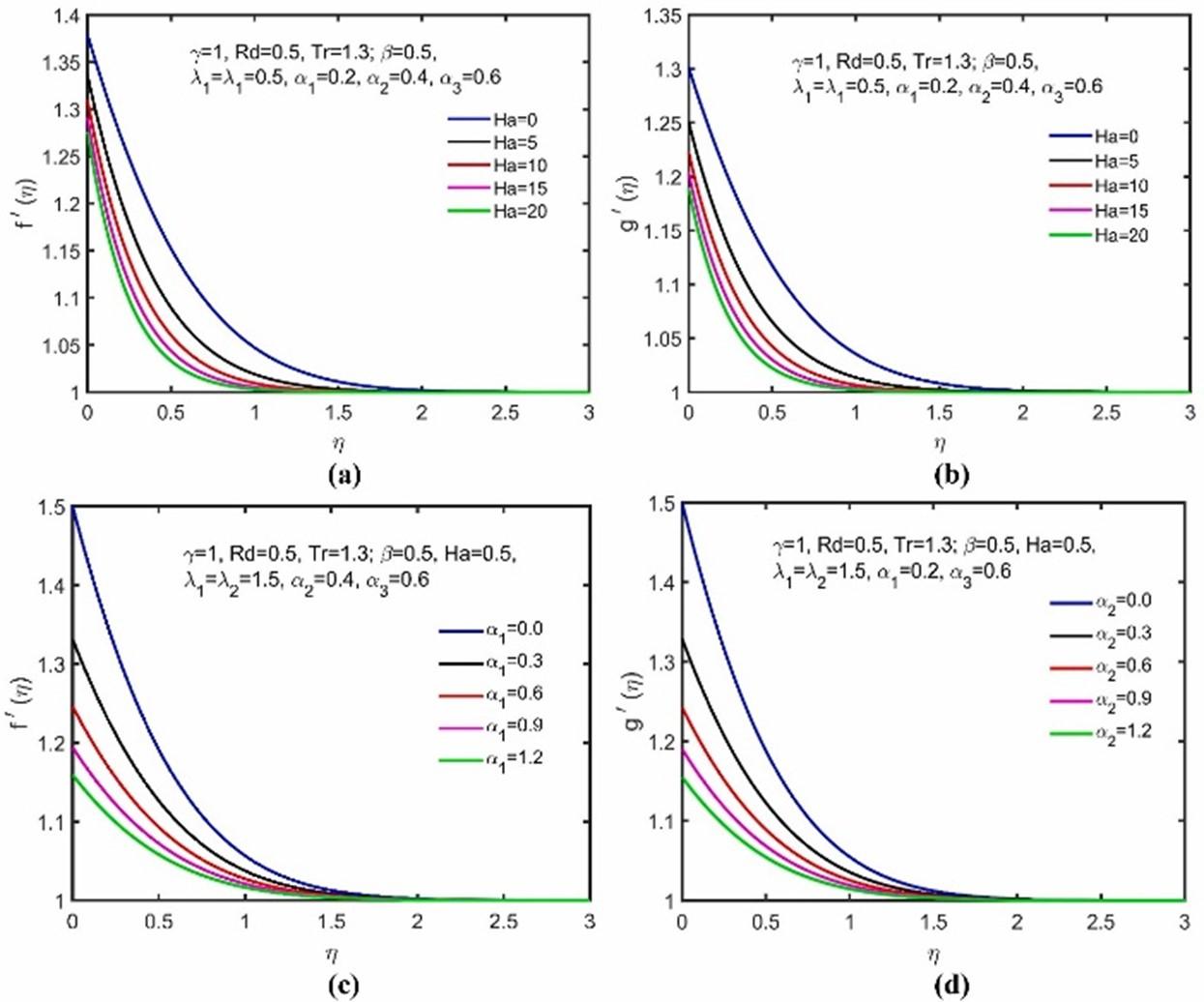
FEM computations and Taguchi optimization in nonlinear radiative MHD MWCNT-MgO/EG hybrid nanoliquid flow and heat transfer over a 3D wedge surface.
Dr. Puneet Rana, Dr. Gaurav Gupta and their team recently published a paper in Thermal Engineering [IF: 6.268]. Their study examines heat transport in hybrid nanofluids on wedge surfaces. It investigates the characteristics of thermal radiative heat transport and rheological properties of MWCNT-MgO/EG nanofluid. The effects of a variable magnetic field and slip boundary conditions are considered. The study uses similarity transformations and the Galerkin finite element method for solving the governing equations. Optimal parameter settings for maximum heat transport rate are determined using the Taguchi method. The temperature jump condition has the highest contribution, and nonlinear thermal radiation enhances heat transfer.